Matrix algebra with R
Goals:
1) Learn how to perform basic matrix operations
2) Learn how to compute basic statistics for multivariate data
Assignments:
1. Download the data set “longley” from the R data base and learn about this
data set
from R-help.
2. Find the variance-covariance matrix S for this data set.
3. Find the correlation matrix r for this data set.
4. Find the standard deviation matrix V1/2.
5. Show numerically that
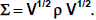
6. Find the deviation vectors di for GNP, Unemployment, and Population; show
that the
length of a deviation vector is proportional to the variance of the
corresponding data set.
7. Plot scatterplot and statistical distance ellipses for pairs GNP-Unemployment
and GNP-Population.
8. Find the eigenvalues and eigenvectors for the 2x2 variance matrices in 7.
Reports: Printed reports are due on Thursday, February 12, 2009.
Report preparation: Consider each report as a
mini-paper. It should NOT be long, but it should
provide a reader with all background information about the problem and methods
you are using.
Review the necessary theoretical material (use formulas if needed), describe the
data. Do not
insert the R-output in your report; instead, summarize it in tables or text in a
nice readable form. If
you feel some parts of the output should be included, put them in Appendix. Put
your name on
the title page.
Remarks:
· Install libraries NOT included in a standard R package: Matrix, car, and
stats.
· R-codes used for class presentations are available on the course Web page.
The sample code (posted on the course web site)
illustrates the following topics in vectormatrix
operations:
1. Vectors and Matrices
1. Defining vectors and matrices
2. Element-wise operations
3. Matrix operations
4. Transposition
5. Determinant
6. Inverse matrix
2. Positive-definite matrices, Quadratic forms
1. Eigenvalues and eigenvectors (spectral decomposition)
2. Illustration of constant-distance ellipses
3. Statistics
1. Random matrices
2. Mean for multivariate data
3. Variance-covariance
4. Sample variance via matrix operators
#=================================================#
# STAT 755 #
# MATRIX ALGEBRA with R #
#=================================================#
#=================================================
# Install libraries ...
#=================================================
library(Matrix) # ... for matrix operations
library(car) # ... for ellipse plots
library(stats) # ... for statistical operations
#==========================================
# Defining vectors and matrices
#==========================================
# Vectors
#---------------
x<-c(1, 2, 3)
y<-c(4, 5, 6)
ones<-rep(1,3)
# To make sure R respects vector dimensions,
# save them as matrices
#----------------------------------------------
x<-as.matrix(x)
y<-as.matrix(y)
ones<-as.matrix(ones)
# Matrices
#----------------------------------------------
A<-matrix(c(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6), byrow=T, ncol=3)
A
A[1,1]
A[1,]
A[,1]
B<-matrix(c(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6), byrow=F, ncol=3)
B
D<-diag(c(1,2,3)) # diagonal matrix
I<-matrix(rep(1,9),ncol=3) # matrix of all ones
#==============================================
# Basic operations with vectors and matrices
#==============================================
# Transpose operation
#-------------------------
t(A)
t(B)
t(D)
t(I)
# Element-wise operations
#-------------------------
A+B
A-B
A*B
A/B
A^B
x+y
x-y
x*y
x/y
y^x
# Matrix and vector operations
#--------------------------------------------------
A%*%B # will give an error message: non-conformable
A%*%t(B)
t(A)%*%B
t(B)%*%A
B%*%t(A)
x%*%t(y)
t(x)%*%y
t(x)%*%t(A)
B%*%D # multiplies each column of B by a number
diag(c(3,4))%*%B # multiplies each row of B by a number
# Determinant of a matrix
#-------------------------
det(D)
det(I)
# Inverse matrix
#--------------------------
Di<-solve(D)
D%*%Di
Di%*%D
# In the example below, you can create an
almost-singular matrix
# (I+N) by choosing small variance for the noise matrix N and
# see what happens with the inverse
#----------------------------------------------------------------
N<-matrix(rnorm(9,sd=1),3,3)
Ii<-solve(I+N)
(I+N)%*%Ii
Ii%*%(I+N)
# Eigenvalues and eigenvectors
#---------------------------------
eigen(D)
N<-matrix(rnorm(9,sd=1),3,3)
eigen(N)
# Positive-definite matrices, Quadratic forms
#------------------------------------------------------------
A<-matrix(rnorm(4),2,2) # random matrix
A<-A%*%t(A) # positive-definite matrix
det(A)
e<-eigen(A)
e
e$vectors %*% diag(e$values) %*% t(e$vectors)
# the same as A
A
ellipse(c(0,0),A,3,add=FALSE,xlim=c(-5,5),ylim=c(-5,5))
ellipse(c(0,0),A,2,add=TRUE)
ellipse(c(0,0),A,1,add=TRUE)
#================================
# STATISTICS
#================================
# Random matrix
#--------------------------------
x<-matrix(rnorm(6), ncol=2)
x
t(x)
# Notice: mean(x) DOES NOT produce what we
want!!!
#--------------------------------------------------
mean(x)
#-----------------------------------
n<-dim(x)[1]
ones<-matrix(rep(1,n),ncol=1)
ones
mu<-t(x) %*% ones / n
# Variance/st.dev of a vector
#-----------------------------------
x
var(x[,1])
var(x[,2])
sd(x[,1])
sd(x[,2])
var(x[,1], x[,2]) # covariance
# Variance-covariance matrix
#----------------------------
var(x)
# Correlation matrix
#----------------------------
cor(x)
# Deviations
#-----------------------------------------------
d1<-x[,1]-mu[1]*ones
d2<-x[,2]-mu[2]*ones
d1
d2
t(d1)%*%d2 # produces biased version of
variance
(n-1)*var(x[,1], x[,2])
#=============================
# Sample variance-covariance
#=============================
# 3x3 matrix of 1s
#------------------
ones%*%t(ones)
# identity matrix
#------------------
diag(3)
# Matrix computation of S (unbiased)
#------------------------------------------------------
(1/(n-1)) * t(x) %*% (diag(3)-(1/n)*ones %*% t(ones)) %*% x
var(x) # ... produces the same result

